Mathematics for Applied Sciences (Osnabrück 2023-2024)/Part I/Exercise sheet 13
- Exercises
Prove the following properties of the hyperbolic sine and the hyperbolic cosine
Prove that in the power series of the hyperbolic cosine the coefficients are if is odd.
Show that the hyperbolic sine is strictly increasing on .
Prove the addition theorems for the hyperbolic functions, that is,
a)
b)
Prove that the hyperbolic tangent satisfies the following estimate
Let
be a polynomial. Show that is an odd function if and only if for all even indices.
Let be a function. Where can you recognize, considering the graph of , whether is an even function?
Let be a function. Where can you recognize, considering the graph of , whether is an odd function?
Show that the sum of two even functions is again even, and that the sum of two odd function is again odd. Can you say something about the sum of an even function and an odd function?
Show that the product of two even functions is again even, that the product of two odd functions is even, and that the product of an even and an odd function is odd.
Show that there exists exactly one function , which is at the same time even and odd.
Let
be a continuous function. Show that one can write
with a continuous even function and a continuous odd function .
What points do you know on the rational unit circle
Describe the upper half of the unit circle and the lower half of the unit circle as graphs of functions.
We consider the rational unit circle
and the line
- Determine the intersection points .
- What is the answer when we consider the situation not over , but over the real numbers ?
- Can you understand the circle without understanding the the real numbers?
- Does there exist a relation with the Intermediate value theorem?
Determine the coordinates of the two intersection points of the line and the circle , where is given by the equation and is given by the center and the radius .
Determine the intersection points of the unit circle and the line which runs through the points and .
Compute the intersection points of the two circles and , where has center and radius and has center and radius .
Let , , and let
be the circle with center and radius . Let denote a line in with the property that there exists at least one point on such that . Show that .
We consider a circle (with radius ) and regular -gons inscribed in the circle.

Suppose that a square is inscribed in the circle. Determine its area and its perimeter.
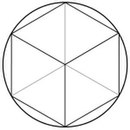
Suppose that a regular -gon is inscribed. Determine its area and its perimeter.
- The area of an inscribed regular -gon is an approximation for the area of the circle and its perimeter is an approximation for the circumference of the circle. Which one is better?
Prove by elementary geometric considerations the Sine theorem, i.e. the statement that in a triangle the equalities
hold, where are the side lengths of the edges and are respectively the opposite angles.
We look at a clock with minute and second hands, both moving continuously. Determine a formula which calculates the angular position of the second hand from the angular position of the minute hand (each starting from the 12-clock-position measured in the clockwise direction).

Dr. Eisenbeis wants to build a bicycle-ramp for her nephews Richy and Franky. The ramp shall rise along a circle arc of the length (everything in meter) and reach a jumping height of (see image). What (implicit) condition does the angle fulfill (the condition on must be such that it could be solved using the bisection method, but this need not be performed)?
Determine the coefficients up to in the series product of the sine series and the cosine series.
Compute
Is the result surprising, how can you explain it?
Show that and holds for all .
Determine the limit of the sequence
Prove that the series
converges.
- Hand-in-exercises
Exercise (3 marks)
Prove that the hyperbolic cosine is strictly decreasing on and strictly increasing on .
Exercise (3 marks)
Determine the coordinates of the two intersection points of the line and the circle , where is given by the equation and is given by the center and the radius .
Exercise (6 marks)


We consider the unit circle, i.e.
We put and , and we define recursively the sequence (in the plane) by
(that is, is the bisection point of the line segment between and ), and is the intersection point of the half-line through and and the circle. We consider the lengths as an approximation for the length of the circle arc between and , and therefore
is an approximation for the length of the half circle arc (that is, ). Since in the computation of the points and the lengths , square roots occure (due to the Pythagorean theorem), we can approximate these by rational numbers only with certain errors.
Write a computer-program (in pseudocode), which computes and prints a sequence of approximations () for . In the computation of , all square roots, which are used in the computation of , shall be computed with steps of Heron's method, starting with the initial value . Also, the program shall use better and better approximations for the auxiliary points, the computation of requires that better and better approximations for are determined.
- The computer has as many memory units as needed, which can contain rational numbers.
- The natural numbers are provided in a data base (they do not have to be computed).
- It can write the content of a memory unit into another memory unit.
- It can do the arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division by a number ) on rational numbers and write the result in another memory unit.
- It can compare the content of memory units and can, depending on the outcome, switch to a certain program line.
- It can print contents of memory units and it can print given texts.
The program shall run to infinity and write down the approximations .
Exercise (5 marks)
Prove the addition theorem
for the sine using the defining power series.
Exercise (3 marks)
Decide whether the sequence defined by
converges in and determine, if applicable, the limit.
Exercise (5 marks)
Consider complex numbers lying in the disc with center and radius , that is in . Prove that there exists a point such that
| << | Mathematics for Applied Sciences (Osnabrück 2023-2024)/Part I | >> PDF-version of this exercise sheet Lecture for this exercise sheet (PDF) |
|---|











![{\displaystyle {}P=\sum _{k=0}^{d}a_{k}x^{k}\in \mathbb {R} [X]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6abf1d478bc7bda3e60c6a47909e90b0a912f610)

















































































