Internet Fundamentals/Databases
This lesson introduces database concepts.
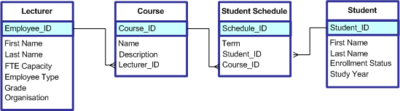


Objectives and Skills
editObjectives and skills for this lesson include:[1][2]
- Recognize essential database concepts.
Readings
editMultimedia
editActivities
edit- Complete one or more of the following tutorials:
- Practice writing single-table SELECT statements using W3Schools SQL TryIt Editor.
- Select all customers (SELECT *).
- Select only customer id and customer name fields (SELECT fields).
- Select customer name, address, city, and postal code for all customers from the United Kingdom (WHERE field = 'value').
- Select contact name and customer name for all customers, sorted alphabetically by contact name (ORDER BY field).
- Count the total number of customers (COUNT(*)).
- Count the number of customers from each country (GROUP BY).
- Count the number of customers from each country and sort the list in descending order by count and ascending order by country in case of a tie (GROUP BY, ORDER BY).
- Count the number of customers from each country and sort the list in descending order by count and ascending order by country in case of a tie, listing only those countries with more than 10 customers (GROUP BY, HAVING, ORDER BY).
- Practice writing multiple-table SELECT statements using W3Schools SQL TryIt Editor.
- Select customer name, order ID, and order date for all customers (INNER JOIN).
- Select customer name, order number, and order date for all customers, renaming the OrderID field as Order Number (INNER JOIN, AS).
- Select customer name, order number, and order date for all customers, sorted by customer name and order number (INNER JOIN, AS, ORDER BY).
- Select order number, order date, product name, and quantity ordered for all customers (INNER JOIN, AS).
- Select order number, order date, product name, quantity ordered, and extended price (quantity * price) for all customers (INNER JOIN, AS, calculated field).
- Select order number, order date, product name, quantity ordered, and extended price for customer 2 (INNER JOIN, AS, calculated field, WHERE).
- Select order number, order date, product name, quantity ordered, and extended price for customer 'Around the Horn' (INNER JOIN, AS, calculated field, WHERE).
- Practice writing INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements using W3Schools SQL TryIt Editor.
- Add a new shipper with ID 4, name 'On Time Delivery', and phone '(503) 555 0123' (INSERT).
- Increase prices on all products by 1 (UPDATE).
- Reduce prices on all products by 1 (UPDATE).
- Change the new shipper's name from 'On Time Delivery' to 'On-Time Delivery' (UPDATE, WHERE).
- Delete the new shipper (DELETE, WHERE).
Lesson Summary
edit- A database is an organized collection of data.[3]
- A relational database is a collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views, and other elements.[4]
- A database-management system (DBMS) is a computer-software application that interacts with end-users, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data.[5]
- A general-purpose DBMS allows the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases.[6]
- Well-known DBMSs include MySQL, PostgreSQL, EnterpriseDB, MongoDB, MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle Database, Sybase, SAP HANA, MemSQL, SQLite and IBM DB2.[7]
- Virtually all relational database systems use SQL (Structured Query Language) as the language for querying and maintaining the database.[8]
- SQL (Structured Query Language) is a special-purpose programming language designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS), or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS).[9]
- Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands include SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.[10]
- The SQL SELECT statement returns a result set of records from one or more tables.[11]
- An asterisk ("*") can be used to specify that the query should return all columns of the queried tables.[12]
- SQL statements are terminated with a semicolon (";").[13]
- A WHERE clause in SQL specifies that a SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) statement should only affect rows that meet specified criteria.[14]
- By default, relational database systems may return data rows in any order, or more specifically, without any order.[15]
- An ORDER BY clause in SQL specifies that a SQL SELECT statement returns a result set with the rows being sorted by the values of one or more columns.[16]
- A SQL JOIN clause combines columns from one or more tables in a relational database.[17]
- An SQL INSERT statement adds one or more records to any single table in a relational database.[18]
- An SQL UPDATE statement changes the data of one or more records in a table. Either all the rows can be updated, or a subset may be chosen using a condition.[19]
- An SQL DELETE statement removes one or more records from a table. Either all records are removed, or a subset may be chosen using a condition.[20]
Key Terms
edit- AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript And XML)
- A set of Web development techniques using multiple Web technologies on the client side to create asynchronous Web applications that can send and retrieve data from a server asynchronously (in the background) without interfering with the display and behavior of the existing page.[21]
- data modeling
- A process used to define and analyze data requirements needed to support the business processes within the scope of corresponding information systems in organizations.[22]
- database
- An organized collection of data.[23]
- database management system (DBMS)
- A computer-software application that interacts with end-users, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data.[24]
- field
- A set of data values of a particular simple type, one for each row of the table.[25]
- foreign key
- A field (or collection of fields) in one table that uniquely identifies a row of another table or the same table.[26]
- index
- A data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure.[27]
- many-to-many relationship
- A type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities A and B in which A may contain a parent instance for which there are many children in B and vice versa.[28]
- one-to-many relationship
- A type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities (see also entity–relationship model) A and B in which an element of A may be linked to many elements of B, but a member of B is linked to only one element of A.[29]
- Open Database Connectivity (ODBC)
- A standard application programming interface (API) for accessing database management systems (DBMS).[30]
- primary key
- A field (or collection of fields) in one table that uniquely identifies a row in the table.[31]
- query
- A precise request for information retrieval with database and information systems.[32]
- record
- A single, implicitly structured data item in a table.[33]
- relational database
- A collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views, and other elements.[34]
- Structured Query Language (SQL)
- A domain-specific language used in programming and designed for managing data held in a relational database management system[35]
- table
- A collection of related data held in a structured format within a database, consisting of columns and rows.[36]
Assessments
editSee Also
editReferences
edit- ↑ CIW: Internet Business Associate Exam Objectives
- ↑ CIW: Internet Business Associate Course Description
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database
- ↑ Wikipedia: Relational database
- ↑ Wikipedia: SQL
- ↑ Wikipedia: Data manipulation language
- ↑ Wikipedia: Select (SQL)
- ↑ Wikipedia: SQL
- ↑ Wikipedia: SQL
- ↑ Wikipedia: Where (SQL)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Order by
- ↑ Wikipedia: Order by
- ↑ Wikipedia: Join (SQL)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Insert (SQL)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Update (SQL)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Delete (SQL)
- ↑ Wikipedia: AJAX
- ↑ Wikipedia: Data modeling
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database
- ↑ Wikipedia: Column (database)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Foreign key
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database index
- ↑ Wikipedia: Many-to-many (data model)
- ↑ Wikipedia: One-to-many (data model)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Open Database Connectivity
- ↑ Wikipedia: Foreign key
- ↑ Wikipedia: Query
- ↑ Wikipedia: Row (database)
- ↑ Wikipedia: Database
- ↑ Wikipedia: SQL
- ↑ Wikipedia: Table (database)