Power Generation/Nuclear Power
Review: Lesson 4
The previous Lesson was about Diesel Power station. The student/User is expected to remember the following from the lesson 4.
- Basics:
- Arrangements:
- Advantages & Disadvantages:
Definition
components that make up a Diesel power station.
How this station measures up
Preview: Lesson 5
This Lesson is about Nuclear Power station. The student/User is expected to understand the following at the end of the lesson.
- Basics:
- Arrangements:
- Advantages & Disadvantages:
Definition
components that make up a Nuclear power station.
How this station measures up

|
Figure 1:Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant Kozloduy Nuclear Power Station, Bulgaria( Click on image to view full size image ) |
Introduction: Nuclear Power station
A Nuclear power station uses nuclear energy for generating electrical energy.
This power station is generally located far from populated areas. This kind of power station can be used to produce large amounts of electrical energy. In most countries these power stations are used as Base load power stations. This is because they can take several days to be warmed up and brought on-line.
Operation
Heavy elements such as Uranium () or Thorium () are subjected to nuclear fission in a reactor to produce steam at high temperatures and pressure.
Steam runs a steam turbine which converts this energy into mechanical energy.
The turbine drives the alternator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Pros & Cons: what this power station presents
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Small amounts of fuel required | Fuel is expensive and hard to recover |
| Power plant requires less space | Capital cost very high |
| Low running charges | Erection & commissioning of plant requires great technical knowledge |
| Economical for producing bulk electrical energy | Fission by-products are generally Radio-active & may cause nuclear pollution |
| Large available deposits of fuel around the world | Maintenance costs are high |
| Reliability of operation | Not suited for varying loads as reactor does not respond to fluctuations |
| Does not require large quantities of water for cooling | Disposal of nuclear by-product is difficult & problematic |
Future generations will want to depend more on this type of electricity generating power station (and other renewable energy sources), due to a fast increasing depletion of fuels(Coal). There are a number of construction projects currently underway for this kind of power station around the world.
|
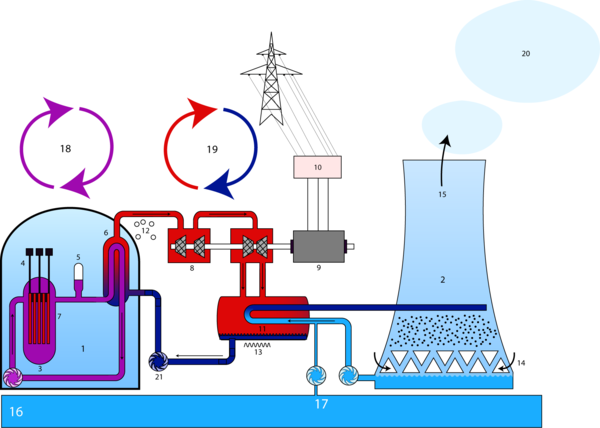
Constituents of Nuclear power station Figure 2 shows a schematic of the general arrangement of a nuclear power station. The constituents of the schematic are labelled in the table below as follows:
To be able to understand the reason why most contries are turning to the wide use of this kind of power station, we must consider the amount of energy produced by the fuel used by this kind of power station.
This schematic diagram must be properly understood. it is the basis upon which nuclear power station designs are done. The individual power station complexity may differ slightly to the shematic and yet over and above that will use the same principle. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTES
References
- This resource is prepared from Lecture notes by Thuvack.
- V.K Mehta & Rohit Mehta :- Principles of Power systems (1st ed.). S.CHAND .ISBN 81-219-2496-0