IT Fundamentals/Business Continuity
This lesson introduces business continuity through IT fault tolerance and disaster recovery.








Objectives and Skills
editObjectives and skills for the business continuity portion of IT Fundamentals certification include:[1]
- Explain business continuity concepts.
- Fault tolerance
- Replication
- Redundancy
- Data
- Network
- Power
- Backup considerations
- Data
- File backups
- Critical data
- Database
- OS backups
- Location
- Stored locally
- Cloud storage
- On-site vs. off-site
- Contingency plan
- Disaster recovery
- Data restoration
- Prioritization
- Restoring access
- Fault tolerance
Readings
editMultimedia
editActivities
edit- Research cloud-based backup storage providers for your home or work environment. What service would you use? How much would it cost? If you don't already have an off-site backup solution, create one now.
- Research redundant Internet service providers for your home or work environment. What service would you use (wired, wireless, etc.)? How much would it cost? Would this be a good investment?
- Consider disaster recovery options for your home or work environment. If you were to lose access to all existing technology resources, how would you restore service? Describe how you would restore data and Internet access and how you would prioritize service restoration. Would you recommend maintaining a hot, warm, cold, or standby solution? Why?
Lesson Summary
editFault Tolerance
edit- Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of (or one or more faults within) some of its components.[2]
- Replication provides multiple identical instances of the same system or subsystem, directing tasks or requests to all of them in parallel, and choosing the correct result on the basis of a quorum.[3]
- Redundancy provides multiple identical instances of the same system and switching to one of the remaining instances in case of a failure (failover).[4]
- Redundant resource needs include:[5]
- Data
- Network
- Power
- A backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event.[6]
- Backup options include full, incremental, differential, and copy.[7]
- A full backup contains a complete copy of the source taken at a specific point in time.[8]
- An incremental backup stores data changed since a reference point in time.[9]
- A differential backup saves only the data that has changed since the last full backup.[10]
- Some filesystems have an archive bit for each file that says it was recently changed. Some backup software looks at the date of the file and compares it with the last backup to determine whether the file was changed.[11]
- Full and incremental backups clear the archive bit. Differential and copy backups do not change the archive bit.[12]
- Backup considerations include:[13]
- Data
- File backups
- Critical data
- Database
- OS backups
- Location
- Stored locally
- Cloud storage
- On-site vs. off-site
- A contingency plan is a plan devised for an outcome other than in the usual (expected) plan. It is often used for risk management for an exceptional risk that, though unlikely, would have catastrophic consequences.[14]
Disaster Recovery
editKey Terms
edit- RAID ("Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks" or "Redundant Array of Independent Disks")
- A data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both.[17]
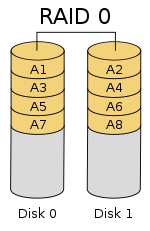
- RAID 0
- Consists of striping, but no mirroring or parity.[18]
- RAID 1
- Consists of data mirroring, without parity or striping.[19]
- RAID 5
- Consists of block-level striping with distributed parity.[20]
- RAID 10
- Consists of a striped set of mirrored drives.[21]
- UPS (uninterruptible power supply)
- An electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails.[22]
Assessments
editSee Also
editReferences
edit- ↑ CompTIA: IT Fundamentals (ITF+) Exam Objectives FC0-U61
- ↑ Wikipedia: Fault tolerance
- ↑ Wikipedia: Fault tolerance
- ↑ Wikipedia: Fault tolerance
- ↑ CompTIA: IT Fundamentals (ITF+) Exam Objectives FC0-U61
- ↑ Wikipedia: Backup
- ↑ Wikipedia: Backup
- ↑ Wikipedia: Backup
- ↑ Wikipedia: Backup
- ↑ Wikipedia: Backup
- ↑ Wikipedia: Backup
- ↑ Wikipedia: Backup
- ↑ CompTIA: IT Fundamentals (ITF+) Exam Objectives FC0-U61
- ↑ Wikipedia: Contingency plan
- ↑ Wikipedia: Disaster recovery
- ↑ CompTIA: IT Fundamentals (ITF+) Exam Objectives FC0-U61
- ↑ Wikipedia: RAID
- ↑ Wikipedia: RAID
- ↑ Wikipedia: RAID
- ↑ Wikipedia: RAID
- ↑ Wikipedia: RAID
- ↑ Wikipedia: Uninterruptible power supply