Human vision and function/Part 1: Perception of objects/Bovine (cow) eye dissection activity
For this activity, you will be using your observations to make inferences from the audio-visual material and your own experimentation that will enable you to consider:
- Describing the orientation within the body and central nervous system (CNS)
- Anatomy of the eye
- The refractive surfaces of the eye, including density and curvature
- Sensitivity of sensory cells within the eye
Watch the video Cow's Eye Dissection. Once you have watched the dissection, answer the questions below.
Orientation of structures within the body and Central Nervous System
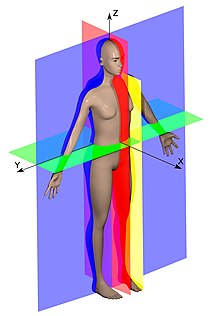
editFirst question to consider: Why might a systematic language be necessary to describe orientation within the body and CNS? Consider this image of the human anatomy planes. The pre-reading from topic 1 will help you answer this.
Anatomy of the eye and the refractive surfaces of the eye (including their density and curvature)
editThe video “Cow's Eye Dissection” demonstrates the three-dimensional structure of the cow eye; highlighting similarities & differences with the human eye.
The external structures described include the:
- cornea
- sclera
- periorbital fat
- extraocular muscle attachment
- optic nerve
The internal structures described include the:
- posterior chamber (vitreous humour & tapetum)
- anterior chamber (aqueous humour, ciliary body & iris)
The functions of the lens are demonstrated:
- magnification of print
- accommodation (increasing curvature of the lens)
Questions
editAnswer the following questions after watching the video:
- What are the horizontal & vertical dimensions of the cow eye and how do they differ from the human eye?
- Which structures are found at the front (ventral) surface of the eye?
- The sclera is opaque and the cornea and lens are transparent. Why is this the case?
- Describe the shape and anatomical position of the lens. What could happen if the lens is not transparent?
- How will the shape of the lens influence refraction of light through the eye and why is the print magnified through the lens??